三角形の面積の計算方法(三角形の面積を計算する)
三角形の面積を求めるには、底辺の半分を取り、高さをかけるのが一般的です。しかし、知っている情報によっては、三角形の面積を計算するのに使える公式は他にもたくさんあるのです。三角形の辺と角の情報を使えば、高さが分からなくても面積を計算することができる...。
方法1 方法1/4:ベースと高さの使い分け
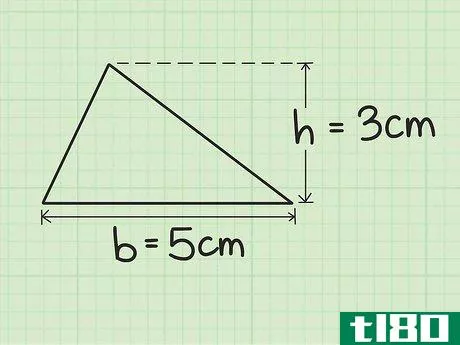
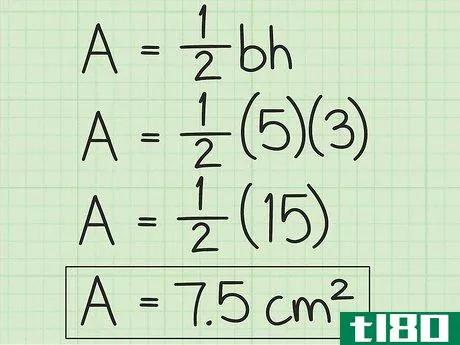
- 1 三角形の底辺と高さを求めなさい。底辺は三角形の辺の1つです。高さは、三角形の最も高い点の寸法です。底辺から反対側の頂点に垂線を引くことで求めることができます。この情報から、あるいは長さを測ることができるはずです。例えば、底辺の長さが5cm、高さが3cmの三角形があるとします。
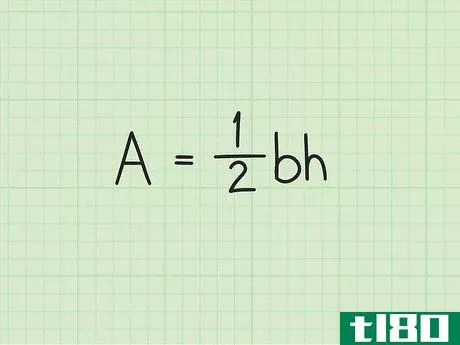
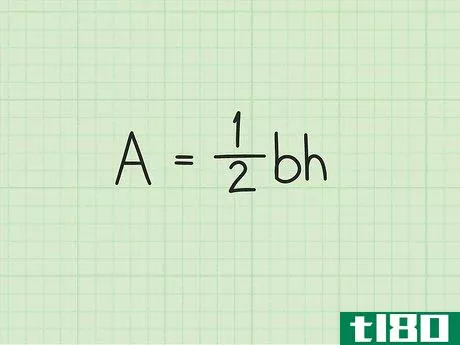
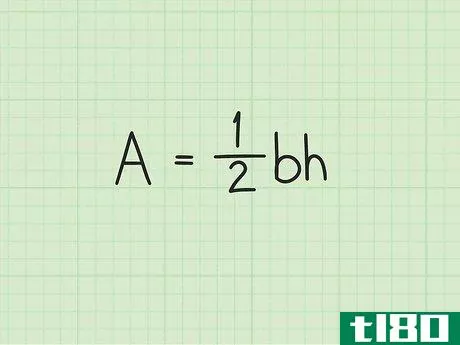
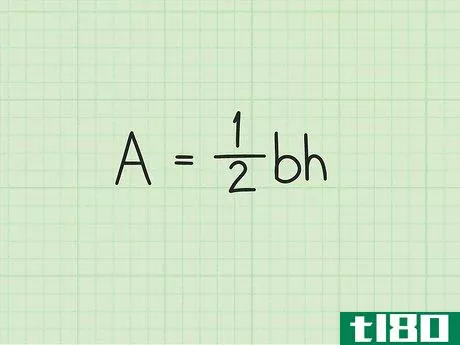
- 2 三角形の面積の公式を確立する。式は Area=12(bh){displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {1}{2}}(bh)} で、b{displaystyle b}は三角形の底面の長さ、h{displaystyle h}は三角形の高さです。
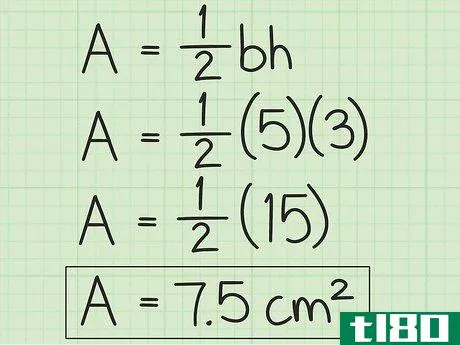
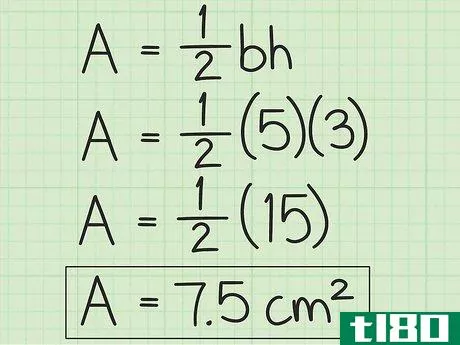
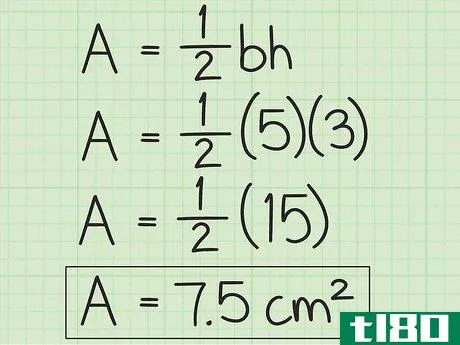
- 3 計算式に底辺と高さを入れる。この2つの値を掛け合わせ、その積に12{displaystyle {frac {1}{2}}を掛けます。}これで、三角形の面積が平方単位で求まる。例えば、底辺5cm、高さ3cmの三角形の場合、次のように計算します。 area=12(bh){}displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {1}{2}}(bh)}Area=12(5)(3){}displaystyle {text{Area}={afrac {1}{2}(5)(3)}Area=12(15){displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {1}{2}(15)}Area=7.5{displaystyle {text{Area}=7.5}So are area of triangle with 5 base of 3 cm and height is 7.5{displaystyle {text{Area}}=7.5}...の三角形は7.5平方センチメートルの面積を持つ。
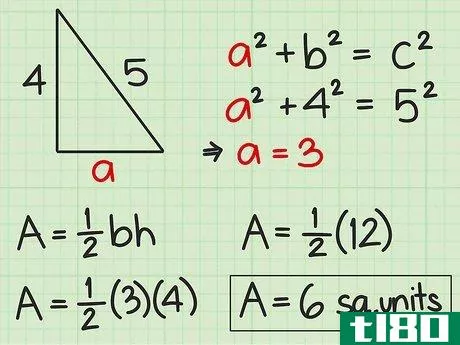
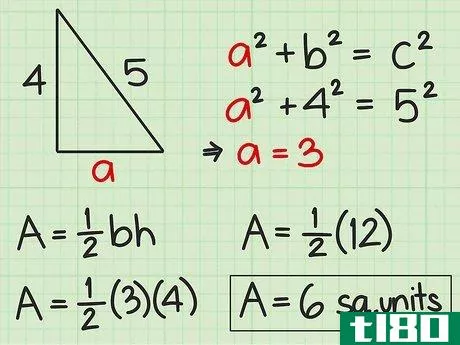
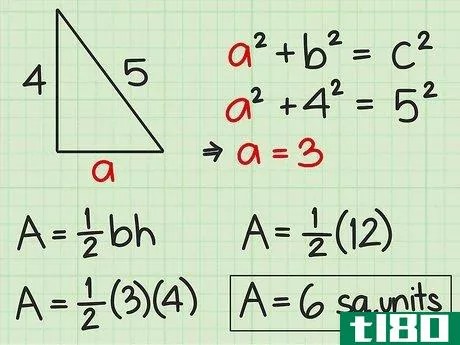
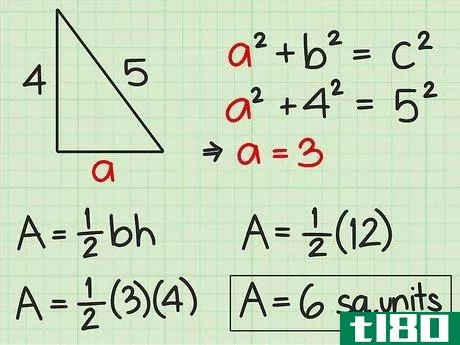
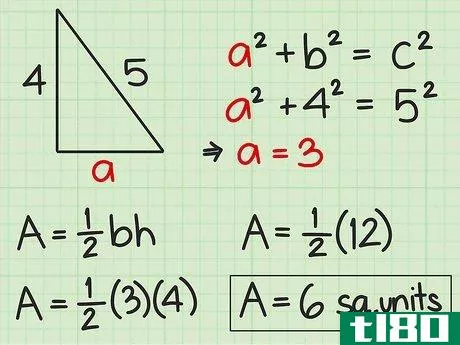
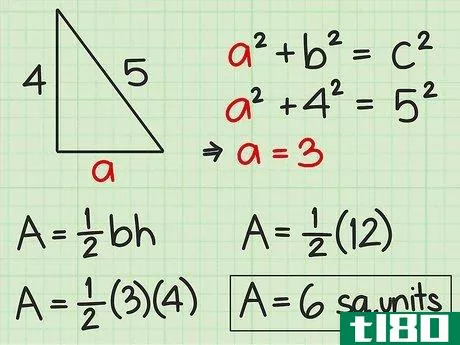
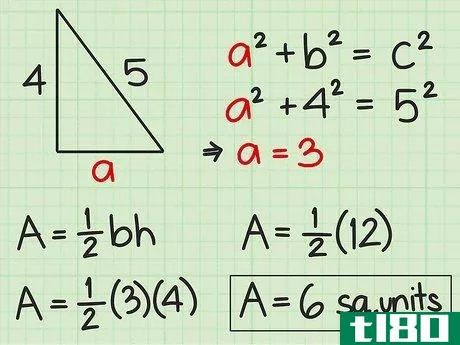
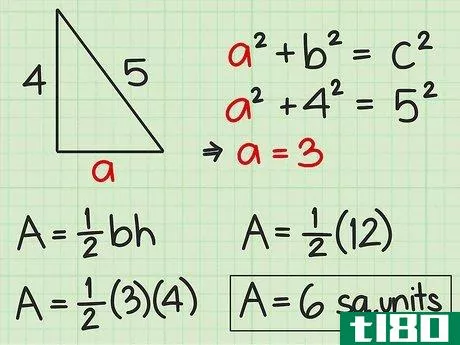
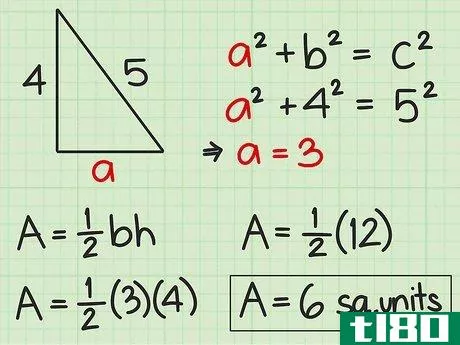
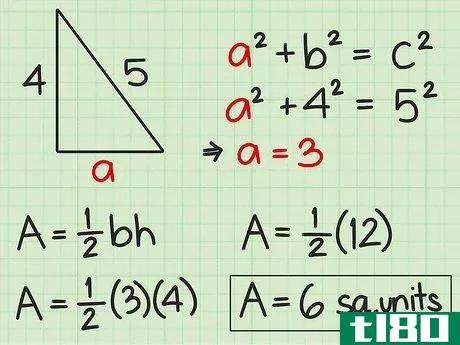
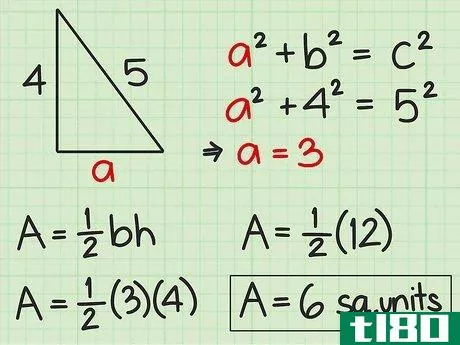
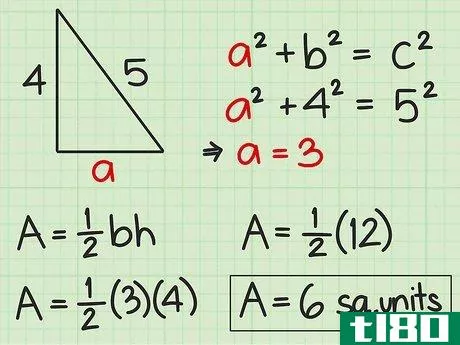
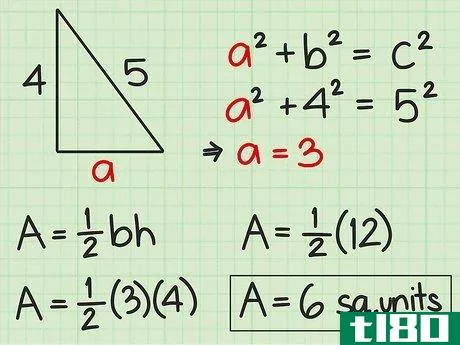
- 4 直角三角形の面積を求めよ。直角三角形の2辺は直角なので、直角の1辺が三角形の高さになる。反対側がベースとなります。したがって、高さや底面の記載がなくても、辺の長さが分かれば求めることができる。したがって、面積を求めるには Area=12(bh){displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {1}{2}}(bh)} という公式を使うことができます。また、一辺の長さと斜辺の長さがわかっている場合にも、この公式を使うことができます。斜辺とは、直角三角形において、直角の反対側にある最も長い辺のことです。ピタゴラスの定理(a2+b2=c2{displaystyle a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2})を使って、直角三角形の足りない辺の長さを求めることができることを覚えておいてください。例えば、三角形の斜辺を辺cとすると、高さと底辺は残りの2辺(a、b)になります。a2+b2=c2 {displaystyle a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}a2+42=52 {displaystyle a^{2}+4^{2}=5^{2}a2+16=25 {displaystyle a^{2}=5c2}、b^{2}=4cm、pythagorean theorem=1c1} {displaystyle a^{1}=2cm}。a^{2}+16=25}a2+16-16=25-16{\displaystyle a^{2}+16-16=25-16}a2=9{\displaystyle a^{2}=9}a=3{\displaystyle a=3}ここで、底辺と高さを代入して、2つの垂直な辺(aとb)を面積の公式に差し込むことができます。 area=12(bh){}displaystyle {}text{Area}={}frac {1}{2}}(bh)}Area=12(4)(3){}displaystyle {}text{Area}={}str...{Area=12(12){displaystyle {text{Area}}={displaystyle {text{Area}}=6} {displaystyle {text{Area}}=6
方法2 方法2/4:エッジレングスの使用
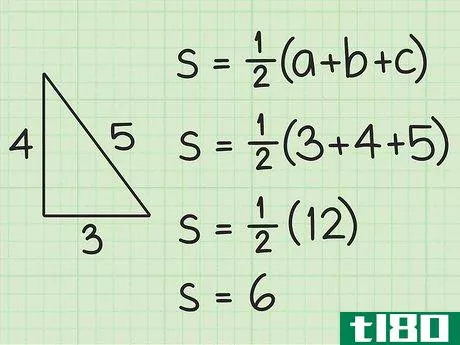
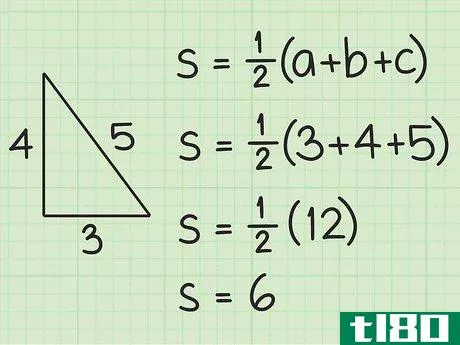
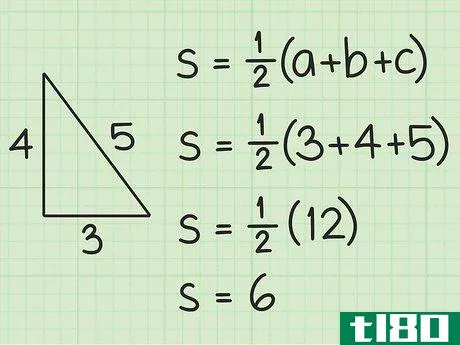
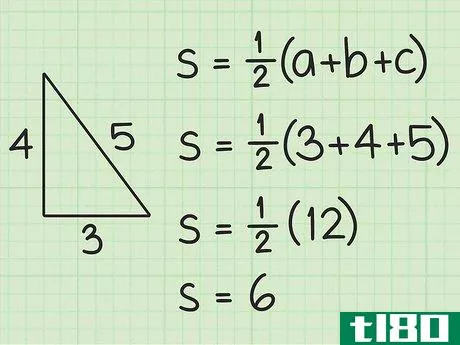
- 1 三角形の半円周を計算する。図形の半周は外周の半分に相当する。半周を求めるには、まず三角形の3辺の長さを足して周囲長を計算します。次に、12{displaystyle {frac {1}{2}}を掛けます。例えば、三角形の3辺の長さが5cm、4cm、3cmであれば、半周は次のようになる。 s=12(3+4+5){displaystyle s={frac {1}{2}}(3+4+5)}s=12(12)=6{displaystyle s={frac {1}{2}}(12)=6} とする。
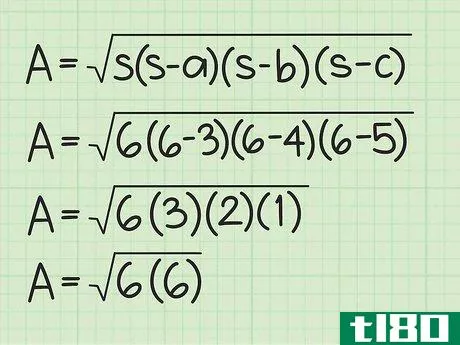
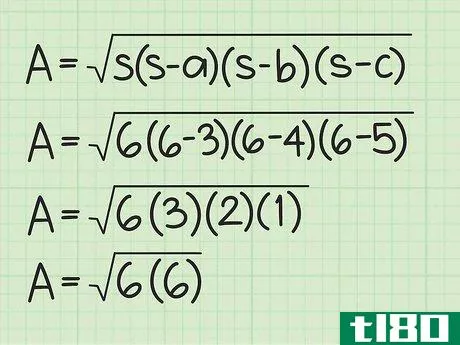
- 2 ヘロンの公式を確立する。式は Area=s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c){displaystyle {text{Area}}={sqrt {s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}} で、s{displaystyle s} は三角形の半周、a{displaystyle a}, b{displaystyle b} は三角形の半周である。displaystyle b}とc{displaystyle c}は三角形の辺の長さです。
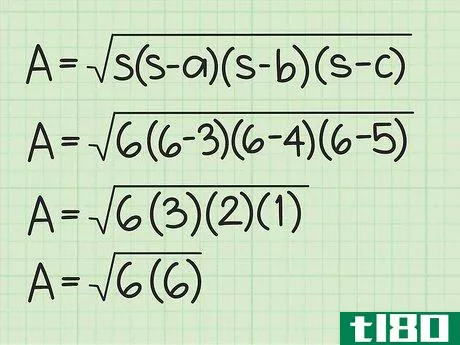
- 3 半円周と辺の長さを計算式に入れる。半周を式中のs{displaystyle s}の各インスタンスに置き換えてください。例えば、Area=s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c){displaystyle {text{Area}}= {sqrt {s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}}Area=6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5){displaystyle {text{Area}}={sqrt {6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5)}}}
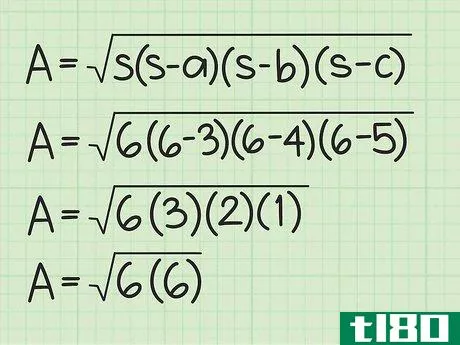
- 4 括弧内の値を計算する。半円周から各辺の長さを引きます。そして、この3つの値を掛け合わせる。例えば Area=6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5){displaystyle {text{Area}}={sqrt {6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5)}}Area=6(3)(2)(1){ のような場合です。\ㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤ
- 5 ルート記号の下にある2つの値を掛け合わせる。そして、それらの平方根を求めます。例: Area=6(6){displaystyle {text{Area}}={sqrt {6(6)}}Area=36{displaystyle {text{Area}}={sqrt {36}}Area=6{displaystyle {text{Area}}=6}} だから、AREA=6。この三角形の面積は6平方センチメートルである。
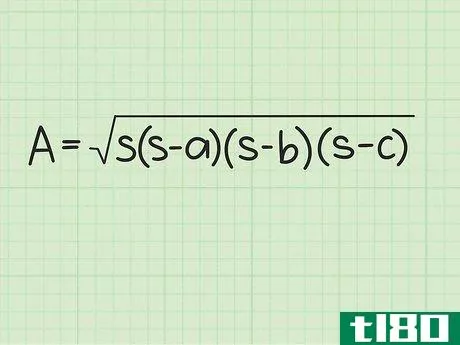
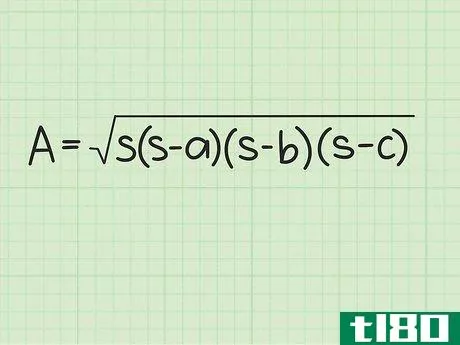
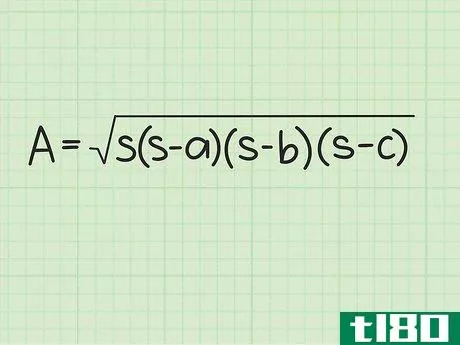
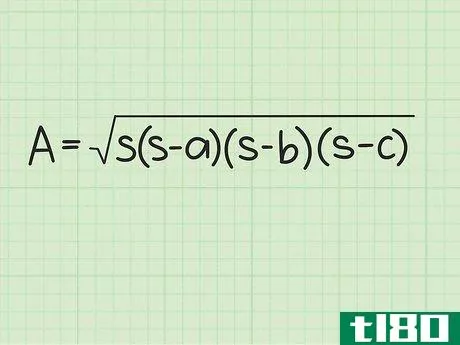
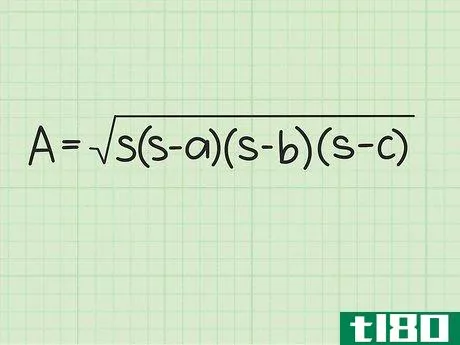
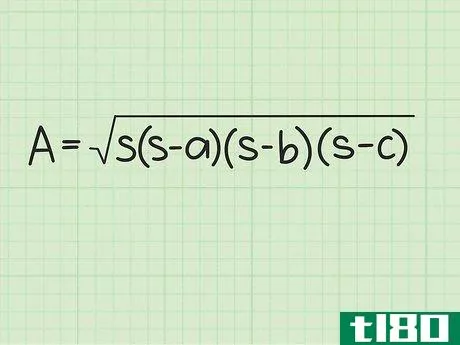
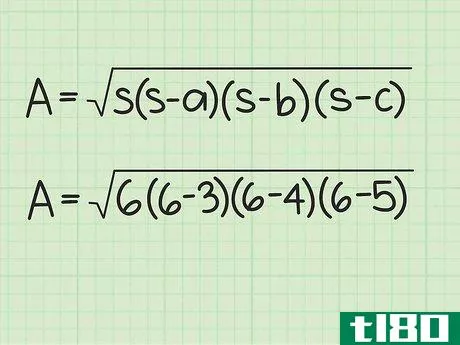
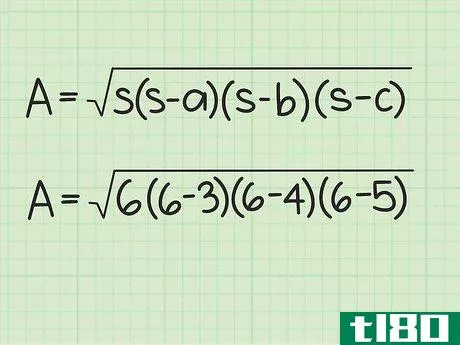
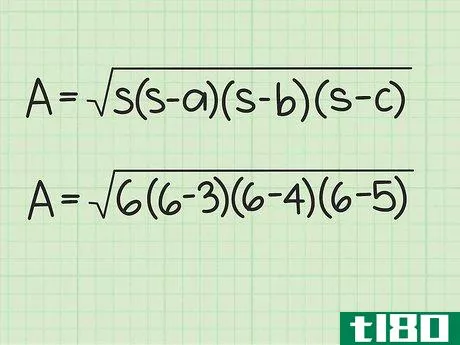
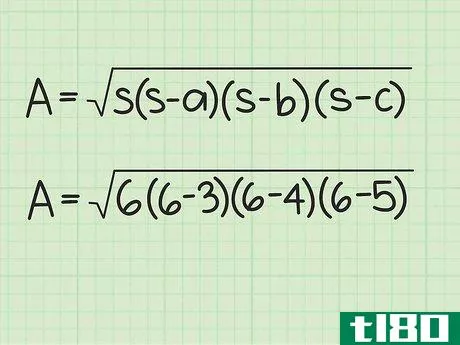




方法3/4:正三角形の一辺を利用する方法
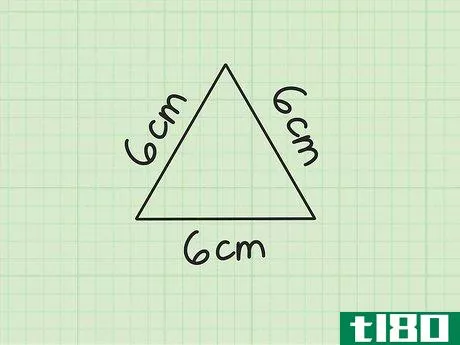
- 1 三角形の一辺の長さを求めなさい。正三角形は、3つの辺の長さと3つの角度が等しいので、1つの辺の長さがわかれば、3つの辺の長さがすべてわかるのです。例えば、3辺の長さがすべて6cmの三角形があるとします。
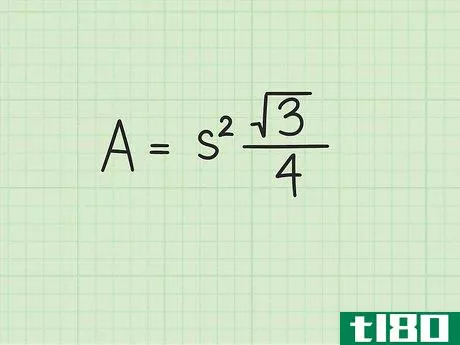
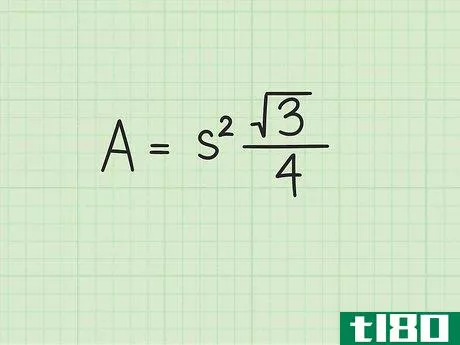
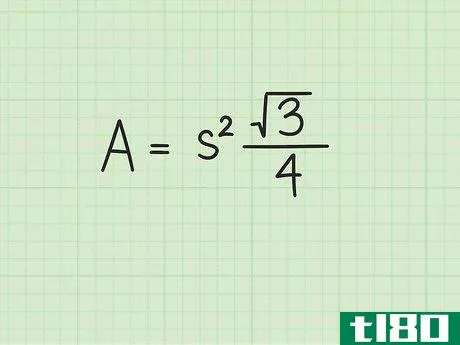
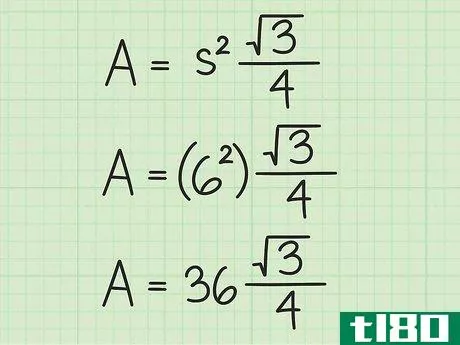
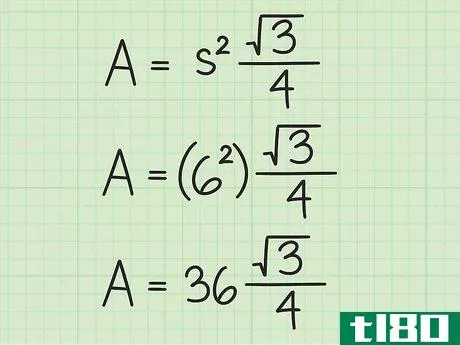
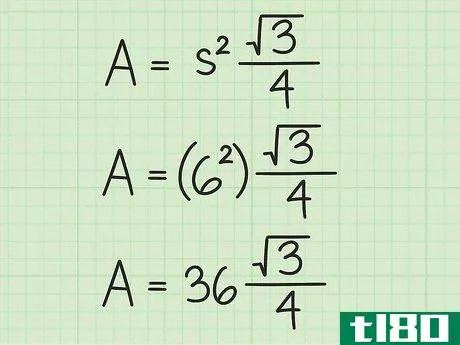
- 2 正三角形の面積の公式を確立する。式はArea=(s2)34{displaystyle {text{Area}}=(s^{2}){frac {sqrt {3}}{4}}で、s{displaystyle s}は正三角形の一辺の長さと同じである。
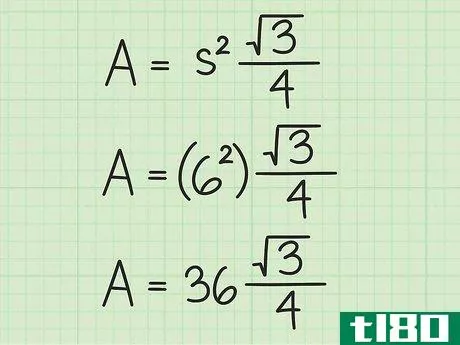
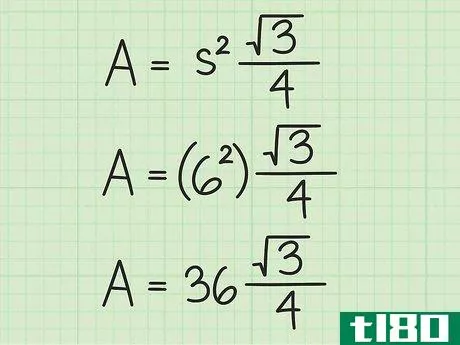
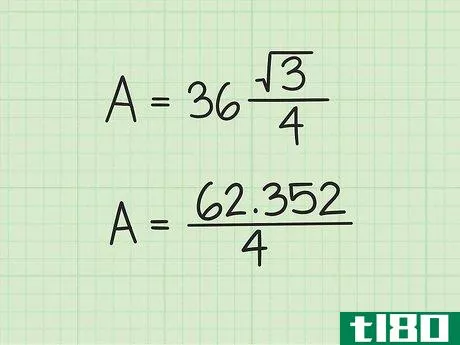
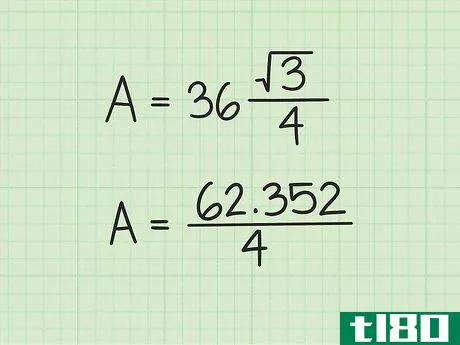
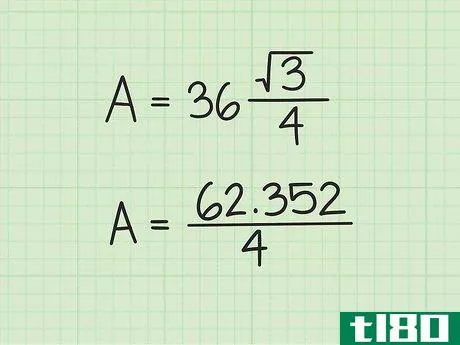
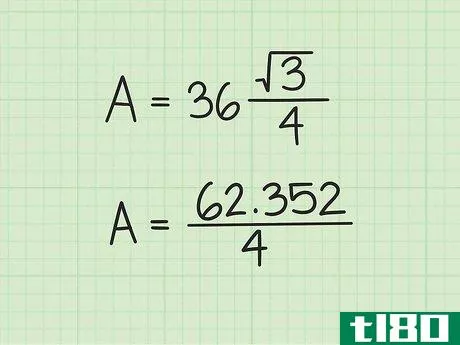
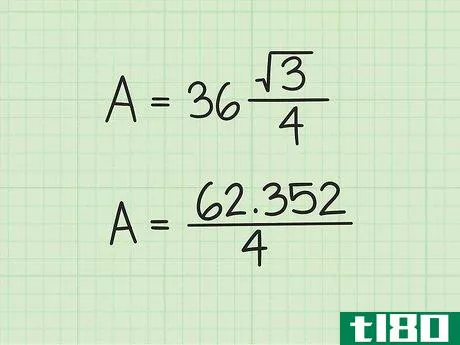
- 3 計算式に辺の長さを入れる。変数s{displaystyle s}を置き換えてから、値を二乗していることを確認してください。例えば、正三角形の辺の長さが6cmの場合、次のように計算します。 area=(s2)34{displaystyle {}text{Area}}=(s^{2}){}frac {}sqrt {3}}{4}}Area=(62)34{displaystyle {}text{Area}=(6^{2}){frac {sqrt {3}{4}}Area=(36)34{displaystyle {text{Area}=(36){frac {sqrt {3}{4}}}Area}} を表示します。
- 4 2乗を3倍する{displaystyle {sqrt {3}} {displaystyle{sqrt}}。より正確な答えを得るためには、電卓の平方根機能を使うとよいでしょう。そうでなければ、3{displaystyle {sqrt {3}}の丸めた値として1.732を使用することができます。例: Area=(36)34{displaystyle {text{Area}}=(36){frac {sqrt {3}}{4}}Area=62.3524{displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {62.352}{4}}}.
- 例えば: Area=62.3524{displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {62.352}{4}}Area=15.588{displaystyle {text{Area}}=15.588} だから、6cmの辺を持つ正三角形の面積は約15.59cm2である。.



方法4 方法4:三角関数の利用
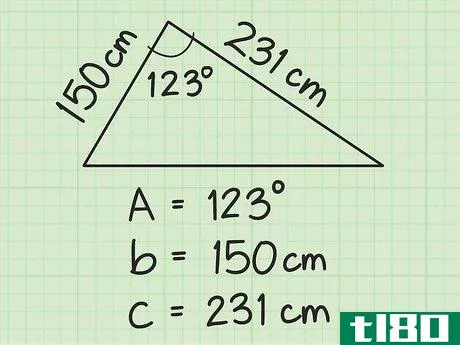
- 1 隣り合う2つの辺の長さと含まれる角度を求めなさい。隣接辺とは、三角形の頂点で交わる2つの辺のことです。含まれる角度は、この2つの辺の間の角度である。例えば、隣り合う2つの辺の長さが150cmと231cmの三角形があるとします。その間の角度は123度。
- 2 三角形の面積を表す三角形の公式を確立する。式は Area=bc2sinA{displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {bc}{2}}sin A} であり、 b{displaystyle b} と c{displaystyle c} は三角形の隣接する辺、 A{displaystyle A} はそれらの間の角度を示しています。
- 3 計算式に辺の長さを入れる。変数b{displaystyle b}とc{displaystyle c}を置き換えることを確認してください。例えば、それぞれの値を掛け合わせ、2で割る。Area=bc2sinA{displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {bc}{2}}sin A}Area=(150)(231)2sinA{displaystyle {text{Area}}={frac {(150)(231)}{2}}sin A} があります。Area=(34. 650)2sinA{displaystyle {text{Area}={frac {(34,650)}{2}}sin A}Area=17,325sinA{displaystyle {text{Area}=17,325sin A}}のようになります。
- 4 角度の正弦を式に挿入する。例えば、123度の角度の正弦は0.83867なので、次のような式になります。 Area=17,325sinA{displaystyle {text{Area}}=17,325sin A}Area=17,325(.83867){displaystyle {text{Area}}=Area} は、この式で示されます。17,325(.83867)}
- 5 この二つの値を掛け合わせる。これで、三角形の面積が平方単位で求まる。For example: Area=17,325(.83867){displaystyle {text{Area}}=17,325(.83867)}Area=14,529.96{displaystyle {text{Area}}=14,529.96}.したがって、三角形の面積は約14,530平方センチメートルとなる。


















- なぜベースハイトの計算式がそうなっているのか、よくわからないという方のために、簡単に説明します。同じ三角形をもう一つ作り、それを二つ並べると、長方形(直角三角形が二つ)または平行四辺形(直角でない三角形が二つ)になります。長方形や平行四辺形の面積を求めるには、底辺と高さを掛け合わせればよい。三角形は長方形や平行四辺形の半分なので、底辺の半分に高さをかけたものを解かなければなりません。
- 2022-03-11 16:44 に公開
- 閲覧 ( 12 )
- 分類:教育