黑色金属之间的差异(differences between ferrous metals)和有色金属(non-ferrous metals)的区别
黑色金属与有色金属
The quality of every material c***tructed depends on its foundation. As today’s 技术 advances, we often see new things being built such as towering buildings and long bridges. In the past, these structures were built with fragile wood. But since humans are quite discontented, they explore and devise new and sturdier materials like metals. Though metals are chemical elements found in nature, humans keep on enhancing their forms to maximize their use. Metals can be subdivided into two groups which are called ferrous metals and non-ferrous metals.
We all know that metals are malleable yet sturdy. These lustrous metals are very good conductors of heat and electricity which make them very 本质的 in today’s living. But what exactly are the differences between ferrous and non-ferrous metals?
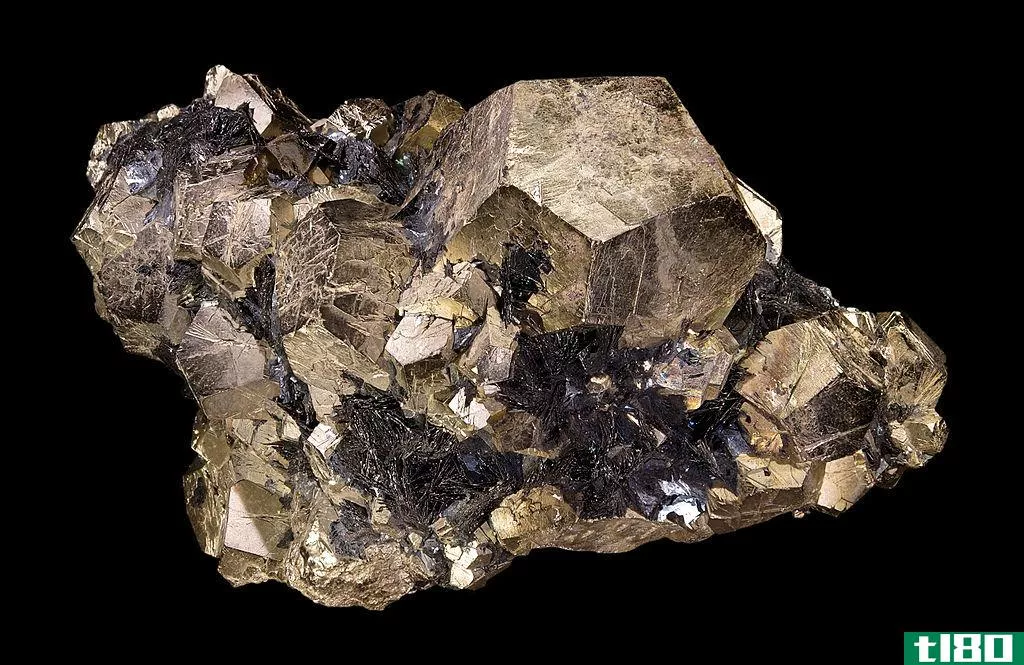
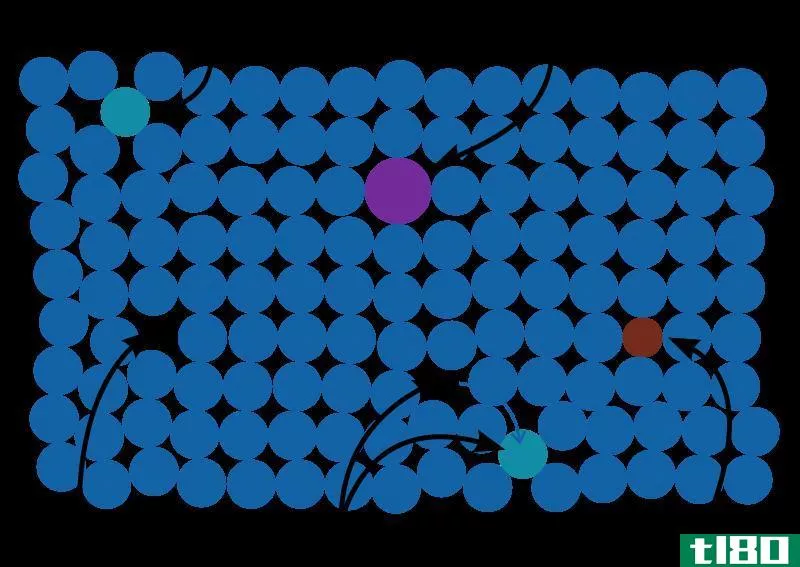
Ferrous metals contain iron. The word “ferrous” has its roots from the Latin word “ferrum” which means “anything that contains iron.” Specific examples of ferrous metals are: wrought iron, stainless steel, and carbon steel. Since ferrous metals contain iron, they are magnetic. This property is the major difference between ferrous metals and non-ferrous metals. Ferrous metals are preferred in building sturdy, strong iron fences and walls, gates, and other materials made with ferrous metal alloys.
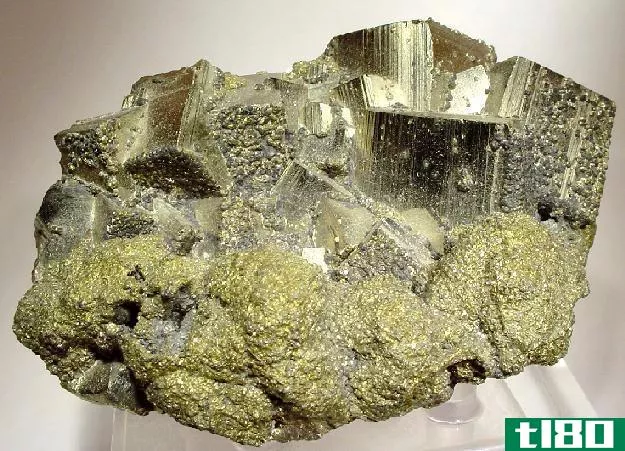
If ferrous metals have magnetic properties, non-ferrous metals are known for their lighter weight yet higher strength. Specific examples of non-ferrous metals are: brass, aluminum, and copper. Since non-ferrous metals are also non-magnetic in nature, they have higher resistance to corrosion with increased melting points. They are more preferred in electronic applicati***. If you would take a closer look at most electrical wiring, it is made mostly of copper, which is a non-ferrous metal.
We have said earlier that ferrous metals are magnetic, but it depends on the amount of iron these metals contain. The best example of this is stainless steel. This type of ferrous metal is not magnetic in nature because it undergoes a different process. In order to make it non-magnetic, it is soaked in nitric acid to get rid of its iron content, thus only the nickel remains. Even if the iron of the stainless steel is purposely removed, it is still classified as a ferrous metal.
If non-ferrous metals are very resistant to corrosion, ferrous metals are not. This corrosion takes the form of rust, the reddish and brownish substance on the surfaces of ferrous metals. This happens because of the presence of moisture in the air causing the ferrous metals to rust.
Summary:
-
金属有两大类:黑色金属和有色金属。金属通常是坚固的、可延展的和可延展的。
-
“铁”一词来自拉丁语“铁”,意思是“任何含有铁的东西”
-
黑色金属是一种含铁的金属,而有色金属则不含铁。
-
黑色金属具有以下特性:磁性和抗腐蚀性较差。
-
有色金属具有以下特性:本质上无磁性,随着熔点的增加,抗腐蚀性更强。
-
黑色金属的磁性有一些例外。不锈钢不是磁性的,因为它的铁是特意去除的,使之成为“不锈钢”
-
黑色金属的具体例子有:熟铁、不锈钢和碳钢。有色金属的具体例子有:黄铜、铝和铜。
-
黑色金属优先用于建造坚固、坚固的铁栅栏和墙壁、大门以及其他由黑色金属合金制成的材料。有色金属主要用于电气和电子应用。
- 发表于 2021-06-24 10:52
- 阅读 ( 374 )
- 分类:化学
你可能感兴趣的文章
离子键合(ionic bonding)和金属键合(metallic bonding)的区别
...属键合的关键区别在于,离子键合发生在正离子和负离子之间,而金属键合发生在正离子和电子之间。 正如美国化学家G.N.Lewis所说,当原子的价壳层中含有8个电子时,原子是稳定的。大多数原子的价壳层中的电子少于8个(周期...
- 发布于 2020-10-24 01:03
- 阅读 ( 859 )
碱金属(alkali metals)和碱土金属(alkaline earth metals)的区别
...碱土金属都是元素周期表中的前两类,碱金属和碱土金属之间的区别是任何化学学生都感兴趣的课题。碱金属和碱土金属是“S-块”元素,因为这两类元素的最外层电子都在S-亚壳层中。 碱金属和碱土金属都是良好的电导体和热...
- 发布于 2020-10-24 18:18
- 阅读 ( 864 )
第1组金属(group 1 metals)和过渡金属(transition metals)的区别
...nguish them by exposing a sample to a Bunsen burner. 此外,第1组金属之间存在一些周期性变化。例如,当进入该族时,元素的原子尺寸增大,熔点和沸点降低,密度增加,第一电离能增加,反应性降低,等等。 什么是过渡金属(transition metal...
- 发布于 2020-10-25 06:27
- 阅读 ( 586 )
金属(metal)和重金属(heavy metal)的区别
...子而形成阳离子。因此,它们是正电的。我们把这些原子之间形成的键叫做金属键。在这些键中,材料从外壳释放电子,这些电子分散在金属阳离子之间。因此,它们被称为离域电子的海洋。我们把电子和阳离子之间的静电相互...
- 发布于 2020-11-02 22:22
- 阅读 ( 421 )
铁质(ferrous)和有色金属矿产(non-ferrous minerals)的区别
...色金属矿物是根据铁含量对矿物进行的最简单分类之一。黑色金属和有色金属矿物的主要区别在于它们的成分;黑色金属矿物含有铁,而有色金属矿物不含铁。然而,这两种矿物都有独特而非常重要的工业应用。含铁矿物有:赤...
- 发布于 2020-11-03 01:31
- 阅读 ( 320 )
金属过剩缺陷(metal excess defect)和金属缺陷(metal deficiency defect)的区别
...的额外阴离子引起的。 以下是金属过剩缺陷和金属缺陷之间的差异汇总表。 总结 - 金属过剩缺陷(metal excess defect) vs. 金属缺陷(metal deficiency defect) 金属缺陷是由于晶格中存在或不存在阳离子或阴离子而产生的。金属过剩缺陷与...
- 发布于 2021-03-04 17:18
- 阅读 ( 359 )
铁(iron)和金属(metal)的区别
...、氖和氟等非金属物质。金属又可分为贱金属、贵金属、黑色金属和贵金属。铁属于黑色金属。 综上所述,人们不能真正指出两者之间的区别,因为铁是称为金属的大集团的一部分。 摘要 1.金属是指在地球上发现的大量元素,...
- 发布于 2021-06-23 06:13
- 阅读 ( 991 )
焊接(soldering)和钎焊(brazing)的区别
...s compared to soft soldering. The process of melting the filler material between the metals parts to be joined is called ‘wetting’. This metal, once cooled, stays at the joint under tensile strength. 什么是钎焊(brazing)? 这是一种焊接工艺,用熔化的金属将两个或多个金...
- 发布于 2021-06-27 09:25
- 阅读 ( 599 )
金属的(metallic)和非金属矿物(non-metallic minerals)的区别
金属的主要区别(main difference metallic) vs. 非金属矿物(nonmetallic minerals) 矿物是一种化合物,以土状物质的形式自然存在,在自然界中是无机的。矿物的化学和物理性质,以及它们的地质位置,使它们彼此不同。岩石的形成...
- 发布于 2021-06-27 11:17
- 阅读 ( 449 )
离子共价(ionic covalent)和金属键(metallic bonds)的区别
...什么是金属键?–定义、形成、性质 4. What is the difference between Ionic Covalent and Metallic Bonds? 什么是离子键(ionic bonds)? Certain atoms tend to donate or receive electr*** in order to become more stable by completely occupying their outermost orbit. Atoms with very few...
- 发布于 2021-06-28 11:41
- 阅读 ( 816 )