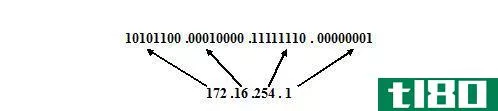
不同类型的局域网ip地址代表什么?

当你开始学习IP地址时,一开始要知道具体的地址代表什么以及为什么这样做可能会有点混乱。有鉴于此,今天的超级用户问答帖子帮助好奇的读者进一步了解IP地址。
今天的问答环节是由SuperUser提供的,SuperUser是Stack Exchange的一个分支,是一个由社区驱动的问答网站分组。
图片由CLUC(Flickr)提供。
问题
超级用户读者Flare Cat想知道不同类型的LAN IP地址代表什么?:
I have seen LAN IP addresses in the following ways/forms:
- 10.0.0.*
- 192.168.0.*
- 192.168.1.*
- 192.168.2.*
- 127.0.0.* (this one usually ends with a 1 and I am not sure if it is a LAN address or not, since I normally see it with proxy stuff)
Why are there different forms of LAN IP addresses and what do they represent (mean)?
不同类型的局域网IP地址代表什么??
答案
超级用户贡献者Abraxas为我们提供了答案:
There are many questi*** that deal with this, but here is a crash course on what are called Private IP Addresses, as defined in RFC 1918.
IP addresses were broken up into what are called classes as seen here. This is no longer used (replaced with Classless Inter-Domain Routing, or CIDR for short), but may help in understanding different sizes of networks:
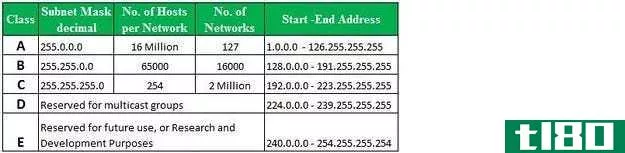
There are a couple of basic distincti*** regarding addresses. You have what are called networks, network addresses, public addresses, private addresses, and subnets.
In short, your computer gets an IP address which resides in a particular IP network. Your computer’s IP address and your network’s address (usually defined in your local router) are private addresses. Private addresses differ from public addresses in that private addresses are not assigned to public networks. For instance, if you ping google.com, you will receive a resp***e from the public address which google.com resolves to. That is a public address. There are some networks which are “special” and do not get assigned publicly; they are called private IP addresses. For more information, read here: What is a Private IP Address?
Here is a list of the private network ranges:
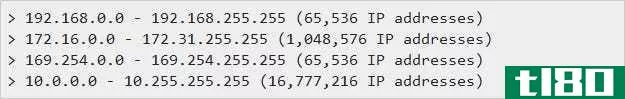
The easiest way, I think, to visualize this is to imagine the following. Your Internet service provider gives you a single IP address, “50.100.101.154”, for example. This is plugged into the modem/router for your home and is the public interface’s IP address. However, you have more than one device you want on your network, so what your modem/router does is it creates an “internal” network. Say it picks the number “192.168.1.0” for the network and it is a standard netmask (read related links to find out more).
This means that you can plug in devices inside of your router and give them any IP address which fits this pattern: “192.168.1.1-254”. The last octet (space after the last period) is your “available range” of host IP addresses. There are some special IP addresses (network addresses, broadcast addresses, etc.), but if you do not use a “0” or a “255”, you will be fine in most cases.
So, the short answer is, “10.x.x.x, 192.168.x.x, and 172.16-31.x.x” are all IP addresses that you can use in your own home network which will never conflict with public IP addresses. This is important for the following reason:
When you try to go to a website, say google.com, and your browser contacts a DNS server on the Internet and says ‘Where is google.com?’, it gets a resp***e back in the form of an IP address. The resp***e is basically, “If you want to get to google.com, then go to 8.8.8.8.” Your browser then sends a request to “8.8.8.8” and loads whatever page is there.
What if you used “8.8.8.8” for an IP address in your home network? Well, you might have an issue because your router may say, “I know where 8.8.8.8 is, it is right over there!” and then you end up losing access to google.com because you cannot get out of your network and resolve the correct “8.8.8.8” address. Since private IP address ranges are designated for private use only, public websites should never use them and therefore you should never look up a website address (outside of your LAN) which points to one of them.
“127.0.0.1” is a special type of address called your “localhost” address (I will not go in to it here). It does cover the whole 127 range: “127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255”. Think of it as a way to give a device its own IP address without anyone or anything else being able to do things with that address.
有什么要补充的解释吗?在评论中发出声音。想从其他精通技术的Stack Exchange用户那里了解更多答案吗?在这里查看完整的讨论主题。
- 发表于 2021-04-09 22:09
- 阅读 ( 235 )
- 分类:互联网
你可能感兴趣的文章
ip地址(ip)和mac地址(mac address)的区别
...**商分配。MAC地址在OSI模型的数据链路层起作用,并作为局域网(LAN)中较低层的每个适配器的唯一标识。 每个MAC地址由48位组成,上半部分包含适配器**商的ID号,下半部分包含**商分配给每个网络适配器的唯一序列号,并存储...
- 发布于 2020-11-04 20:17
- 阅读 ( 337 )
什么是dmz?如何在网络上配置dmz?
...器)隔离在它们自己的逻辑子网中,可以保护内部网络或局域网(LAN)的其余部分,以防出现危害。 ...
- 发布于 2021-03-11 08:47
- 阅读 ( 738 )
网络101:以太网、局域网及其工作原理
...络上”是既定的。多年来,企业一直在使用基于以太网的局域网来实现这一目标。。。但是“局域网”和“以太网”不是同义词。 ...
- 发布于 2021-03-14 04:20
- 阅读 ( 263 )
局域网和广域网在联网方面有什么区别?
如果你已经涉足计算机网络,你很有可能会遇到“局域网”和“广域网”这两个术语。然而,这两个术语的含义是什么?当你比较局域网和广域网时,它们的区别是什么? ...
- 发布于 2021-03-26 15:03
- 阅读 ( 305 )
互联网是如何工作的?
... 相关报道:什么是网络中立? 你可能在家里有自己的“局域网”,它由所有连接到路由器的设备组成,路由器连接到互联网。“因特网”一词指的是一个由“相互连接的计算机网络”组成的世界性系统。 这就是互联网的全部—...
- 发布于 2021-04-06 17:58
- 阅读 ( 241 )
如何在互联网上分享你的雷击游戏
...你就避免了每次你想和你的朋友在线玩的时候都要在本地局域网上查找你电脑的IP地址。 您可以在计算机级别分配静态IP地址,但这并不理想,因为它可能与路由器分配给其他计算机的IP地址冲突。理想情况下,您希望在路由器...
- 发布于 2021-04-08 10:41
- 阅读 ( 195 )
如何通过internet远程打开电脑
...你可以在需要的时候远程打开电脑。 这充分利用了唤醒局域网。尽管它的名字,它可以设置唤醒局域网,这样你就可以发送“魔术包”,将唤醒一台计算机在互联网上。 在局域网上设置唤醒 相关:什么是LAN唤醒,如何启用它...
- 发布于 2021-04-11 08:20
- 阅读 ( 184 )
22个常见网络术语解释
...是康卡斯特,时代华纳,或者任何你每月支付的公司。 局域网 局域网是一个局限于局域网的小型网络。例如,您的家庭网络或办公网络是局域网。 广域网 广域网是一个覆盖范围更广的更大的网络。您的ISP为您提供了与自己的WA...
- 发布于 2021-04-11 08:51
- 阅读 ( 196 )
ipsec协议(ipsec)和gre考试(gre)的区别
...:Internet、Intranet和Extranet。 也有几种不同的联网方法:局域网(LAN),它是用在一个小的地区,如在一个建筑物;城市城域网;大面积使用的广域网,以及无线局域网和广域网。 这些网络,特别是那些使用因特网的网络,利用...
- 发布于 2021-06-23 21:10
- 阅读 ( 195 )
第二层交换机(layer 2 switch)和第三层交换机(layer 3 switch)的区别
...配一个唯一的MAC地址。它利用基于硬件的交换技术来管理局域网中的通信量。由于交换发生在第2层,所以这个过程非常快,因为它所做的只是在物理层对MAC地址进行排序。简单来说,第2层交换机充当多个设备之间的桥梁。 什...
- 发布于 2021-06-25 05:17
- 阅读 ( 614 )