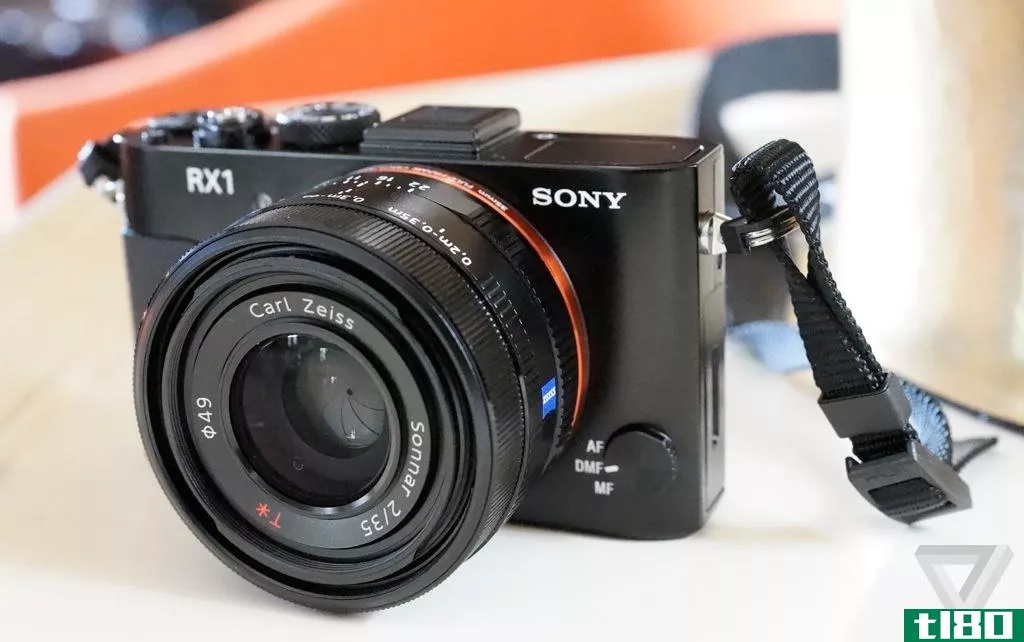
我相机镜头上的字母、缩写和数字代表什么?

快速瞥一眼你相机的镜头,就会发现一大堆字母、数字和缩写词。它们到底是什么意思?如何将代码转换成有用的信息?
今天的问答环节是由摄影交流(Photography Exchange)提供的,摄影交流是Stack Exchange的一个分支,是一个由社区驱动的问答网站分组。图片由美国佳能公司提供。
问题
摄影交流读者Mikal Sundberg对他相机镜头上的标记很好奇。他写道:
Then looking at a lens name there is a lot of acronyms in the name describing it’s features (often specific to the manufacturer).
Examples, Nikon: Nikon AF-S DX 16-85mm VR f/3.5-5.6G IF-ED Nikon AF-I 600mm f/4D IF-ED Nikon AF-S VR Micro-NIKKOR 105mm f/2.8G IF-ED
Examples, Canon: Canon EF 85mm f1.2L USM Mark II Canon 70-300mm f/4.5-f/5.6 DO IS
Examples, Sigma: Sigma 150mm F2.8 EX APO DG HSM Macro Sigma 70-200mm F2.8 EX DG OS HSM Sigma 50-150mm F2.8 EX DC APO HSM II
How do I decipher the lens names from different manufacturers?
那么你需要什么样的解码环来理解代码呢?
答案
摄影交流撰稿人Jrista提供了一个非常全面的答案。在你找到你的相机设备的具体品牌之前,如果你浏览一下他那篇铺天盖地的文章,我们不会对你进行评判。
Brand Lenses
Most major camera manufacturers offer their own line of lenses. Such lenses tend to follow the most stringent quality guidelines, and often come with a price premium.
Canon Lenses
Canon lenses use the following terms to indicate features of each lens:
- Common
- XYZmm: Focal length
- f/x.y: Maximum aperture
- Focus/Mount Type
- EF: Electronic Focus
- EF-S: Short-Back Electronic Focus
- EF-M: Mirrorless Electronic Focus
- TS: Tilt-Shift
- TS-E: Tilt-Shift, Electronic aperture control
- MP-E: Macro-Photography, Electronic aperture control
- Features
- IS: Image Stabilization
- USM: Auto Focus Type: Ultrasonic Motor
- STM: Auto Focus Type: Stepping Motor
- (Mark) N: Version of lens (Mark II = v2, Mark III = v3, etc., word Mark may not be present)
- DO: Diffractive Optics
- L: Luxury series
- Macro: close focusing, but not necessarily 1:1 magnification
- Softfocus ability to use soft focusing for **ooth dreamy look
- PF Power Focus
Examples
- Canon EF 16-35mm f/2.8 L II USM Lens
- Canon EF 70-200mm f/2.8 L IS II USM Lens
- Canon TS-E 17mm f/4 L
- Canon EF 50mm f/1.2 L USM
- Canon EF-S 10-22mm f/3.5-4.5 USM
Nikon Lenses
Nikon lenses use the following terms to indicate features of each lens:
- Common
- XYZmm: Focal length
- f/x.y: Maximum aperture
- Lens System
- DX: Digital, Short Back
- FX: Full Frame (film or digital)
- Lens Mount
- AI: Automatic Indexing mount (includes metering sensor)
- AI-S: Improved Automatic Indexing mount
- IX: Lenses designed specially for APS film SLR-s; their rear end protrudes too much to allow using them on a 35mm film camera or a dSLR
- Serie E A cheaper serie of AI-S where plastic replaced some metal parts. Not designated as Nikkor but “Nikon Lense Serie E”
- Focusing System
- AF: Auto Focus, built into camera
- AF-S: Auto-Focus Silent (Silent Wave Motor, required for bodies without focus motor)
- AF-I: Auto-Focus Internal
- AF-N: Auto-Focus (improved version, rare)
- Features
- Reflex: Catadioptric (mirror) lense.
- D: Distance, communicates focus distance for 3D Matrix metering mode and also for flash autoexposure. All AF-I, AF-S, and G-type lenses are also D-type. (Indicated after the f-number in the name, sometimes designated as AF-D).
- SWM: Silent Wave Motor
- N: Nano-Crystal Coating
- NIC: Nikon Integrated Coating (multicoated lenses)
- SIC: Super Integrated Coating (multicoated lenses)
- VR: Vibration Reduction
- ED: Extra-low Dispersion Glass
- FL: Fluorite. Designated a lens with some element in fluorite instead glass.
- ASP: Aspherical Lens Element
- IF: Internal Focusing
- RF: Rear Focusing
- RD: Rounded diaphragm
- Micro: Enable high reproduction ratio. Typically at 1:1 or 1:2.
- G: No aperture ring (automatic aperture only)
- DC: Defocus Control
- PC: Perspective Control. Lenses with shift feature (older) and newer with tilt as well.
- E: Electronic diaphragm. Some lenses with an electronic diaphragm. Only supported by bodies from D3 and after.
- P: CPU enabled version of AI-S lenses (Sometimes designated as AI-P)
Examples
- Nikon AF 85mm f/1.8
- Nikon AF 85mm f/1.8D
- Nikon AI 500mm f/4.0 P
- Nikon AF-S DX 16-85mm VR f/3.5-5.6G IF-ED
- Nikon AF-I 600mm f/4D IF-ED
- Nikon AF-S VR Micro-NIKKOR 105mm f/2.8G IF-ED
Olympus 4/3 lenses
- Common
- XYZmm: Focal length
- 1:x.y: Maximum aperture
- Features
- ED: Extra-low dispersion glass elements
- SWD: Auto Focus Type: Supersonic Wave Drive Motor
- N: Version of lens (II = v2, III = v3, etc.)
Pentax lenses
- Common
- XYZmm: Focal length
- 1:x.y: Maximum aperture
- Focus/Mount Type
- K, M: Manual Focus, Manual/Aperture priority metering
- AF: Early AF system with AF motor and electronics in lens that works only with ME-F body.
- A: Manual Focus, supports Shutter priority and Program exposure metering
- F: Adds Auto Focus to capabilities of A lenses
- FA: Adds ability to communicate MTF to body to capabilities of F lenses
- FAJ: Removes aperture ring from capabilities of FA lenses
- DA: Same capabilities as FAJ, but with reduced imaging circle for digital cameras with APS-C sized sensor
- DA L: Same capabilities as DA lenses, Lighter c***truction
- D FA: Same capabilities as FA lenses, usable on both film and digital cameras
- Features
- AL: Aspherical elements
- ED: Extra-low dispersion glass elements
- SMC: Super multi coating lens coating
- HD: Newer “high grade” multi-layer lens coating
- PZ: Power Zoom
- SDM: Auto Focus Type: Supersonic Drive Motor
- IF: Internal focussing
- WR: Weather Resistant (when matched with weather resistant body)
- AW: All Weather (again when matched with WR body; it’s unclear how if at all this differs from the above)
- ★: High performance, including weather and dust sealing
- Limited: High quality, compact design (primes)
- Macro: 1:1 magnification
- XS: Extra slim, even more compact than Limited
Sony/Minolta Lenses
Sony lenses, previously Minolta lenses, have similar features to Nikon and Canon. Their notation is as follows:
- Common
- XYZ/x.y: Focal length/Maximum Aperture
- Lens Mount Type
- Alpha: α Type Mount
- E: E Type Mount
- Focusing System
- SSM: In-Lens Super-sonic Motor
- SAM: In-Lens Micro Motor
- Features
- G: Gold Series (highest quality)
- (D): Distance Encoding (supports ADI feature of some Sony bodies)
- DT: Digital Technology (optimized for digital cameras)
- APO: Apochromatic correction using AD elements
- HS-APO: High-Speed APO
- AD: Anomalous Dispersion
- OSS: Optical Steady Shot (E-mount only)
- T*: High-performance Coating
- M: 1:1 magnification
- Z: optical engineering by Carl Zeiss
Examples
- Sony Alpha 70-200/2.8 G
- Sony Alpha 28-75/2.8 SAM
- Sony Alpha DT 18-250/3.5-6.3
- Sony E 18-200/3.5-6.3 OSS
- Sony Alpha 100/2.8 Macro
Off-Brand Lenses
Many off-brand lens manufacturers make lenses that fit many types of bodies, including Canon, Nikon, etc.
Sigma Lenses
Sigma lenses use the following terms to indicate features of each lens. They differ slightly in how they denote aperture:
- Common
- XYZmm: Focal length
- Fx.y: Maximum aperture
- Compatible Body Brands
- Sigma
- Nikon
- Canon
- Minolta/Sony
- Pentax
- Kodak (extremely limited)
- Fujifilm
- Olympus (limited)
- Panasonic (very limited)
- Leica (very limited)
- Features
- HSM: Hyper-Sonic Motor
- ASP: Aspherical lens element
- APO: Aphochromatic (low-dispersion) lens element
- OS: Optical Stabilizer
- RF: Rear focusing
- IF: Inner focusing
- CONV: Teleconverter compatible (APO Teleconverter EX), not usually part of the lens name but mentioned in the product description
- EX: Professional lens body finishing and c***truction
- DG: Supports full-frame cameras (newer lenses only, implicit on older models)
- DC: Supports cropped-frame cameras (lightweight c***truction, **aller image circle)
- DN: For mirrorless cameras
- Macro: close focusing, but not necessarily 1:1 magnification
Examples
- Sigma 18-250mm f/3.5-6.3 DC OS HSM
- Sigma 150-500mm f/5-6.3 DG OS HSM
- Sigma 50mm f/1.4 EX DG HSM
- Sigma 105mm f/2.8 EX DG Macro
Tamron Lenses
Tamron lenses use the following terms to indicate features of each lens. Tamron offers a c***iderable degree of functional features and lens types, particularly lens types that affect chromatic aberration:
- Common
- XYZmm: Focal length
- F/x.y: Maximum aperture
- AF: Auto-Focus
- Compatible Body Brands
- Nikon
- Canon
- Minolta/Sony
- Pentax
- Features
- Lens Elements
- XR: Extra Refractive Index Glass (lighter, **aller lenses)
- LD: Low Dispersion (chromatic aberration reduction)
- XLD: Extra Low Dispersion (advanced chromatic aberration reduction)
- ASL: Aspherical (improved focal plane convergence)
- LAH: LD + ASL hybrid lens element
- AD: Anomalous Dispersion (improved control over chromatic aberration)
- ADH: AD + ASL hybrid lens element
- HID: High Index, High Dispersion Glass (minimizes lateral chromatic aberration)
- Functional Features
- VC: Vibration Compensation
- USD: Ultrasonic Silent Drive
- SP: Super Performance (professional line)
- IF: Internal Focusing System
- Di: Digitally Integrated (optimized for use with full-frame digital cameras)
- Di-II: Digitally Integrated (optimized for use with APS-C digital cameras)
- ZL: Zoom Lock (prevents undesired zoom lens barrel extension)
- A/M: Auto-focus/Manual-focus Switch Mechani**
- FEC: Filter Effect Control (controls filter direction when lens hood attached, i.e. for Polarizing filters)
- 1:1 Macro: 1:1 Magnification
- Lens Elements
Examples
- Tamron SP AF17-35MM F/2.8-4 Di LD Aspherical (IF)
- Tamron AF18-200mm F/3.5-6.3 XR Di II LD Aspherical (IF)
- Tamron SP AF180mm F/3.5 Di LD (IF) 1:1 Macro
Tokina Lenses
Tokina lenses use the following terms to indicate features of each lens:
- Common
- VW~XYZmm: Focal length
- f/x.y: Maximum aperture
- AF: Auto-Focus
- Compatible Body Brands
- Nikon
- Canon
- Minolta/Sony
- Pentax
- Features
- AT-X Pro professional line (primes and c***tant aperture zooms)
- AT-X c***umer line (variable aperture zooms)
- AS: Aspherical Optics
- F&R: Advanced Aspherical Optics
- SD: Super Low Dispersion
- HLD: High-Refraction, Low Dispersion
- MC: Multi-Coating
- FE: Floating Element System
- IF: Internal Focus System
- IRF: Internal Rear Focus System
- FC: Focus Clutch Mechani** (allows switching between auto & manual focus)
- One Touch FC: One-Touch Focus Clutch Mechani**
- FX: Full frame
- DX: Digital (cropped frame)
Samyang Lenses
Samyang (also sold as Pro-Optic, Rokinon, Bower) lenses use the following terms to indicate features of each lens:
- Common
- XYZ mm: Focal length
- f/x.y: Maximum aperture
- Compatible Body Brands
- Nikon
- Canon
- Minolta/Sony
- Pentax/Samsung
- Olympus
- Panasonic
- Features
- AE: contains electronic chip to allow Automatic Exposure and iTTL flash metering on a Nikon body
- AS: contains Aspherical element(s)
- Aspherical: contains Aspherical element(s)
- ED: contains extra-low dispersion element(s)
- IF: Internal Focusing
- MC: Multi Coating
- UMC: Ultra Multi Coating
- MFT: designed for Micro Four Thirds systems
- CS VG10 – custom design for Sony Nex-VG10
- Preset: Aperture preset (so you can quickly flick aperture ring between maximum aperture for focusing and desired aperture for shooting; there’s no aperture linkage on a preset lens)
- Mirror: a mirror lens
Examples
- Samyang AE 14 mm f/2.8 ED AS IF UMC
- Samyang 35 mm f/1.4 AS UMC
- Pro-Optic AE 85 mm f/1.4 Aspherical IF
如果你现在抓挠你的头,因为你已经学会了这个词,但你不知道它是什么意思,另一个摄影交流用户哈米什唐纳在这里提供帮助:
The top answer covers the decoding of the letters very well. I thought I might add a few comments as to what some of the features actually mean in terms of c***equences of the features (it took me a while to work out what some of them meant).
Lenses only for reduced frame DSLRs
Most low to mid range DSLRs have a sensor that is **aller than a 35mm film frame – sometimes called “reduced frame” or “cropped sensor”. So using a “full frame” lens will mean lots of extra light around the sensor that isn’t used. You can makes lenses **aller and lighter by reducing the projected image size to fit the sensor size. However using these lenses on a full frame camera would result in the corners of the image being dark – and mostly these lenses won’t fit on a full frame camera.
The “less than full frame” codes are:
- Canon: EF-S (EF for full frame)
- Nikon: DX (FX for full frame)
- Pentax: DA (FA or D FA for full frame)
- Sigma: DC (DG for full frame)
- Sony/Minolta: DT
- Tamron: Di II (Di for full frame)
Image Stabilisation/Vibration Reduction
Image Stabilisation is also called Optical Stabilisation, Optical Image Stabilisation, Optical Steady Shot, Vibration Compensation and Vibration Reduction. Does what it says on the tin basically. (Although note that some DSLR bodies have a form of vibration reduction in the body and so don’t need it in the lens).
- Canon: IS
- Nikon: VR
- Panasonic: OIS
- Sigma: OS
- Sony/Minolta: OSS
- Tamron: VC
Fast and Quiet Focussing Motors
The focussing motors in some lower end lenses can be quite noisy. The higher end lenses are able to focus more quickly (the movements can be more accurately controlled) and are quieter and use less battery. The acronym for it usually includes “Sonic”:
- Canon: USM Ultrasonic Motor
- Nikon: SWM Silent Wave Motor
- Olympus/Zuiko: SWD Supersonic Wave Drive
- Pentax: SDM Supersonic Drive Motor
- Sigma: HSM Hyper-Sonic Motor
- Sony/Minolta: SSM Super-Sonic Motor
- Tamron: USD Ultrasonic Silent Drive
Lens Features
There are a variety of lens features to reduce chromatic abberati*** (where different colours don’t exactly converge) and other imperfecti*** in lens performance. In particular
- aspherical lens elements have a more complex surface profile that can reduce or eliminate spherical aberration and also reduce other optical aberrati*** compared to a simple lens.
- low dispersion glass means that there is a relatively **all difference in the amount different colours bend while going through the glass (technically the refractive index does not vary so much with wavelength), which reduces chromatic aberration.
- apochromatic lens elements are very good at reducing chromatic aberration – they are generally made up of three different materials stuck together.
- Canon: DO Diffractive Optics
- Nikon: ED Extra-low Dispersion Glass, ASP Aspherical Lens Element
- Olympus/Zuiko: ED Extra-low dispersion glass
- Pentax: ED Extra-low dispersion glass, AL Aspherical Lens Element
- Sigma: ASP Aspherical lens element, APO Aphochromatic (low-dispersion) lens element
- Sony/Minolta: AD Anomalous Dispersion, APO Apochromatic correction using AD elements, HS-APOHigh-Speed APO
- Tamron: Aspherical or ASL aspherical lens element, AD Anomalous Dispersion, ADH AD + ASL hybrid lens element, HID High Index, High Dispersion Glass, LD Low Dispersion, LAH LD + ASL hybrid lens element, XLD Extra Low Dispersion, XR Extra Refractive Index Glass
- Tokina: AS Aspherical lens element, F&R Advanced Aspherical lens element, HLD High-Refraction, Low Dispersion, SD Super Low Dispersion
Lens Coatings
There are a variety of lens coatings used to reduce internal reflecti*** and other possible problems. Internal reflecti*** can end up producing ghost images or adding to lens flare. Not all lens manufacturers specify the lens coatings they use.
- Nikon: NIC Nikon Integrated Coating, SIC Super Integrated Coating
- Pentax: SMC Super Multi Coating
- Sony/Minolta: T High-performance Coating
- Tokina: MC Multi-Coating
- Yashica: DSB Single-Coating, ML (later MC) Multi-Layer (later Multi-coating)
Macro
Macro lenses can focus very close to the end of the lens, providing (at least) a 1:1 ratio between the size of the object and the size of the image on the sensor. In plain english, you can take very close up shots of flowers, insects and so on. They are just called Macro (or occasionally Micro), making life easy for once.
Focusing
This includes Internal/Inner Focusing (IF) and (Internal) Rear Focusing (RF or IRF). Both of these reduce the number of individual lenses moving inside the lens. They also mean that the front of the lens will not move in or out, or rotate, during focusing. The lack of rotation can be important if, say, you have a circular polarizing filter, or a graded ND filter fitted to the lens. And the front not moving in or out can be important if the lens is very close to the subject.
High End Lenses
Some manufacturers have a code to indicate their high end lenses:
- Canon: L Luxury
- Pentax: * and Limited
- Sigma: EX Professional EXternal lens body finishing
- Sony: G Gold Series
- Tamron: SP Super Performance
Miscellaneous
Other codes might indicate the mount type (which will indicate whether it will fit your body), whether it will work with a Teleconverter or whether the lens needs the camera body to provide the motor for auto-focussing.
Note that I’m not an expert at this and am happy to integrate clarificati*** left in comments.
有什么要补充的解释吗?在评论中发出声音。想从其他精通技术的Stack Exchange用户那里了解更多答案吗?在这里查看完整的讨论主题。
- 发表于 2021-04-11 16:51
- 阅读 ( 290 )
- 分类:互联网
你可能感兴趣的文章
你还需要知道30个网络俚语和首字母缩略词
...:如果你收到一个你不认识的号码或不在你的联系人名单上的号码的短信,“DIKY”是一个快速询问你是否认识这个人的方法。 ...
- 发布于 2021-03-14 09:26
- 阅读 ( 290 )
数码变焦和光学变焦有什么区别?
变焦,就像很多相机规格一样,比广告宣传让你相信的要复杂一些。像三星这样的智能****商现在都在吹嘘10倍、50倍甚至100倍的变焦。但这有可能吗?让我们看看光学变焦和数码变焦的区别。 缩放实际上是什么意思? 什么是缩...
- 发布于 2021-04-01 19:29
- 阅读 ( 188 )
什么是单反裁剪因子(我为什么要在意)
每次我们谈论数码相机时,都会提到传感器的“裁剪系数”。让我们再深入一点,解释一下为什么它很重要。 不同的摄像头,不同的传感器 数码相机并非都有大小相同的传感器;有两种不同的标准。**商在其专业和高端相机...
- 发布于 2021-04-04 10:26
- 阅读 ( 196 )
什么是测距相机?
...有关摄影的书籍,你可能会遇到一些令人崇敬的提到徕卡相机和其他“测距仪”,它们被许多伟大的街头摄影师使用,比如20世纪中期的亨利·卡地亚·布列松(Henri Cartier Bresson)。我知道当我第一次听说他们的时候我很困惑,因...
- 发布于 2021-04-04 11:13
- 阅读 ( 142 )
如何检查你相机上的序列号
你拥有的每一件相机装备都有一个唯一的序列号来识别它。如果你需要提出保险索赔或报案,你可以用它来证明某个相机或镜头属于你。下面是如何找到你的装备序列号。 最好在你买了一套新的装备后就把你的序列号都写下来...
- 发布于 2021-04-05 05:29
- 阅读 ( 258 )
走出汽车:如何使用您的相机的拍摄模式,更好的照片
如果你想充分利用你的单反相机,最好学习它的不同拍摄模式,而不是只使用全自动所有的时间。尽管表盘周围有很多字母和符号(如M、Av、Tv和P),但事情可能会变得有点混乱。这里有一个第一次的指南,以摆脱自动模式和...
- 发布于 2021-04-08 19:26
- 阅读 ( 162 )
如何利用景深拍摄更好的照片
...意(depth of field and why should i care)? 最简单的说,景深是指相机可用的焦平面(景深)。这个深度是由照片中的物体范围来定义的,这些物体对观看者来说是可以接受的锐利的。离镜头太近或太远的物体落在可接受的锐度范围之外...
- 发布于 2021-04-09 03:42
- 阅读 ( 172 )
别再相信电视的谎言了:关于“增强”图像的真实真相
...还是模拟,都以大致相同的方式工作。让我们考虑一下照相机。当光(我们称之为光子的粒子)与某种生成图像的介质相互作用时,所有的相机都会生成某种图像。在数码相机中,它是一个光电传感器。在胶卷照相机中,它是一...
- 发布于 2021-04-11 02:41
- 阅读 ( 115 )
为什么每个相机都把照片放在dcim文件夹里?
无论是专用数码相机还是Android或iPhone上的相机应用程序,每台相机都会将您拍摄的照片放在DCIM文件夹中。DCIM代表“数码相机图像” DCIM文件夹及其布局来自DCF,这是一个创建于2003年的标准。DCF非常有价值,因为它提供了一个...
- 发布于 2021-04-11 03:10
- 阅读 ( 200 )
我相机镜头上的字母、缩写和数字代表什么?
快速瞥一眼你相机的镜头,就会发现一大堆字母、数字和缩写词。它们到底是什么意思?如何将代码转换成有用的信息? 今天的问答环节是由摄影交流(Photography Exchange)提供的,摄影交流是Stack Exchange的一个分支,是一个由社...
- 发布于 2021-04-11 16:51
- 阅读 ( 290 )